Bioactive lipids - phospholipids including Plasmalogens and PAFs, gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), dihomo-GLA (DGLA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) help cells of the innate immune system - macrophages - with phagocytosis. Targeting membrane sphingolipids and interfering with the virus lipid metabolism could represent a promising path to follow towards the development of COVID-19 treatments.
REFERENCES
Lee SH, Kim KN, Kim KM, Joo NS. Irritable bowel syndrome may be associated with elevated alanine aminotransferase and metabolic syndrome. Yonsei medical journal. 2016 Jan 1;57(1):146-52.
Serra J, Salvioli B, Azpiroz F, Malagelada JR. Lipid-induced intestinal gas retention in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2002 Sep 1;123(3):700-6.
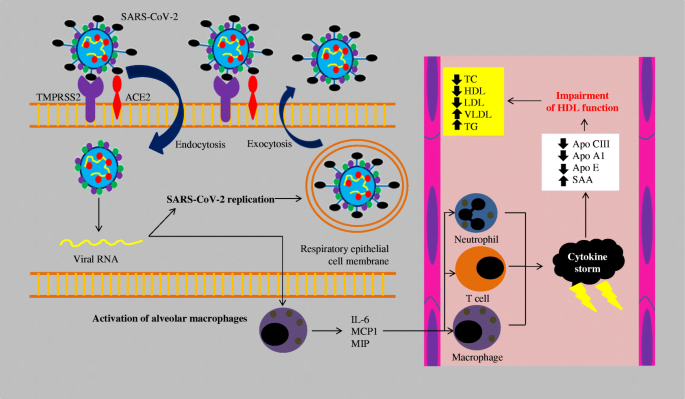
Schwarz B, Sharma L, Roberts L, Peng X, Bermejo S, Leighton I, Casanovas-Massana A, Minasyan M, Farhadian S, Ko AI, Cruz CS. Cutting edge: Severe SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans is defined by a shift in the serum lipidome, resulting in dysregulation of eicosanoid immune mediators. The Journal of Immunology. 2021 Jan 15;206(2):329-34.
Hao Y, Zhang Z, Feng G, Chen M, Wan Q, Lin J, Wu L, Nie W, Chen S. Distinct lipid metabolic dysregulation in asymptomatic COVID-19. Iscience. 2021 Sep 24;24(9):102974.
Surma S, Banach M, Lewek J. COVID-19 and lipids. The role of lipid disorders and statin use in the prognosis of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lipids in Health and Disease. 2021 Dec;20(1):1-4.
Casari I, Manfredi M, Metharom P, Falasca M. Dissecting lipid metabolism alterations in SARS-CoV-2. Progress in Lipid Research. 2021 Feb 8:101092.
Demopoulos CA. Is Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF) a missing link for elucidating the mechanism of action of the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and explaining the side effects-complications of Covid-19 disease?.
Deng Y, Angelova A. Coronavirus-Induced Host Cubic Membranes and Lipid-Related Antiviral Therapies: A Focus on Bioactive Plasmalogens. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 2021 Mar 12;9:551.
Martín-Fernández M, Aller R, Heredia-Rodríguez M, Gómez-Sánchez E, Martínez-Paz P, Gonzalo-Benito H, Sánchez-de Prada L, Gorgojo Ó, Carnicero-Frutos I, Tamayo E, Tamayo-Velasco Á. Lipid peroxidation as a hallmark of severity in COVID-19 patients. Redox biology. 2021 Dec 1;48:102181.
Das UN. Bioactive lipids-based therapeutic approach to COVID-19 and other similar infections. Archives of Medical Science. 2021.